What Is Emotional Intelligence (EI)?
Emotional Intelligence (EI), also known as Emotional Quotient (EQ), refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions — as well as the emotions of others. Unlike Intelligence Quotient (IQ), which measures cognitive ability, emotional intelligence focuses on the emotional and social competencies that influence how effectively we connect, communicate, and collaborate.
The concept gained global recognition in the 1990s after psychologist Daniel Goleman published his landmark book “Emotional Intelligence.” He emphasized that EQ often determines success in life more than IQ because it shapes our relationships, decisions, leadership abilities, and overall mental well-being.
Emotional intelligence allows us to handle stress, adapt to change, empathize with others, and make emotionally informed choices — skills that are essential in every aspect of modern life.
What Defines Emotional Intelligence?
At its core, emotional intelligence involves awareness, regulation, and empathy. These three dimensions allow individuals to perceive emotions accurately, use them to facilitate thought, understand emotional meanings, and regulate emotions effectively.
A person with high emotional intelligence:
- Recognizes their emotions as they arise
- Responds to challenges thoughtfully, not reactively
- Communicates with empathy and active listening
- Builds trust and healthy relationships
- Learns from emotional experiences instead of avoiding them
Researchers describe EI as a set of learnable skills, not an innate trait. This means anyone can develop stronger emotional intelligence with practice, mindfulness, and self-reflection.
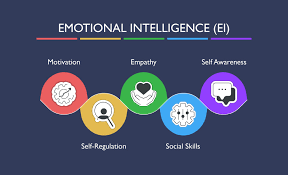
What Are the 5 Elements of Emotional Intelligence?
Daniel Goleman’s model identifies five key components that form the foundation of emotional intelligence.
1. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand your emotions, triggers, and internal states. It helps you stay conscious of how your feelings influence behavior and performance. A self-aware person understands their strengths, weaknesses, values, and motivations, leading to better decision-making and personal growth.
2. Self-Regulation
Self-regulation involves controlling emotional impulses, staying calm under pressure, and thinking before acting. It doesn’t mean suppressing emotions — it’s about managing them constructively. For example, staying composed during workplace stress or handling criticism gracefully are signs of strong self-regulation.
3. Motivation
Motivation in EI is more than ambition; it’s the inner drive to achieve goals with passion and persistence. Emotionally intelligent individuals are self-motivated — they pursue growth, not just rewards. They view setbacks as opportunities for learning rather than failures.
4. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to sense and understand others’ feelings — an essential skill for effective communication and leadership. It allows you to perceive emotional cues, show compassion, and respond appropriately, fostering trust and collaboration in both personal and professional settings.
5. Social Skills
Social skills integrate all the other components of EI. They include clear communication, conflict resolution, cooperation, and influence. People with strong social skills can manage relationships, inspire others, and build cohesive teams.
Together, these five elements form the foundation for emotional resilience, effective leadership, and authentic relationships.
What Are the 4 Pillars of Emotional Intelligence?
Another framework used to describe EI includes four interdependent pillars, which simplify its application in daily life.
1. Self-Awareness
As the cornerstone of emotional intelligence, self-awareness helps us recognize emotions before they control our actions. It encourages reflection and helps us identify patterns in behavior that influence outcomes.
2. Self-Management
This pillar focuses on emotional control, adaptability, and maintaining a positive attitude. It’s what allows professionals to stay composed during challenges, avoiding impulsive reactions that might harm relationships or credibility.
3. Social Awareness
Social awareness expands our focus beyond self. It includes empathy, cultural sensitivity, and awareness of group dynamics. This skill enables effective teamwork and helps leaders connect with diverse audiences.
4. Relationship Management
This pillar integrates all emotional competencies into meaningful social interaction. It’s about influencing, inspiring, and resolving conflicts constructively. People with strong relationship management skills can build trust, lead effectively, and create supportive networks.
How to Master Your Emotions
Mastering your emotions doesn’t mean suppressing them — it means understanding, accepting, and channeling them productively. Here’s how you can build emotional mastery:
1. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness increases awareness of emotional triggers. By observing your thoughts without judgment, you learn to pause before reacting. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or journaling enhance emotional clarity.
2. Identify Triggers and Patterns
Recognize situations or people that evoke strong emotions. Understanding your triggers helps you anticipate reactions and respond thoughtfully instead of impulsively.
3. Reframe Negative Thoughts
Cognitive reframing — a core technique in emotional regulation — involves viewing challenges from a more constructive perspective. Instead of thinking “I failed,” consider “I learned something valuable.”
4. Develop Empathy
Active listening and genuine curiosity about others’ experiences enhance empathy. When you truly understand another’s perspective, emotional conflicts dissolve faster, and collaboration becomes easier.
5. Strengthen Communication Skills
Emotional intelligence thrives on effective communication. Practice expressing emotions clearly yet respectfully. Use “I” statements (e.g., “I feel concerned when…”) to convey feelings without blame.
6. Build Resilience
Resilience means bouncing back from setbacks without losing balance. Emotionally intelligent individuals view adversity as part of growth, focusing on solutions rather than problems.
Benefits of Emotional Intelligence in Life and Work
High emotional intelligence has profound effects on both personal and professional well-being:
- Improved mental health: EI reduces stress, anxiety, and emotional burnout.
- Stronger relationships: Empathy and communication foster connection and trust.
- Effective leadership: Leaders with high EQ inspire loyalty, motivation, and teamwork.
- Better conflict management: Emotional control enables resolution over escalation.
- Enhanced decision-making: Emotionally intelligent individuals combine logic with empathy, resulting in balanced, ethical choices.
In workplaces, emotional intelligence predicts success more accurately than technical skill alone. Teams led by emotionally intelligent leaders often report higher engagement, creativity, and satisfaction.
How to Improve Emotional Intelligence Over Time
Like any skill, emotional intelligence can be cultivated through consistent effort. Here’s how to build it progressively:
- Self-reflect daily: Ask yourself how emotions affected your actions and interactions.
- Seek feedback: Honest feedback from colleagues or mentors helps uncover blind spots.
- Develop empathy: Engage in conversations with diverse individuals to understand different perspectives.
- Regulate stress: Use techniques like breathing exercises, time management, or relaxation routines to maintain balance.
- Learn emotional vocabulary: Accurately naming your emotions increases control and clarity.
- Practice gratitude: Regularly acknowledging positive emotions reinforces optimism and emotional balance.
Conclusion
Emotional Intelligence is not a fixed trait but a lifelong skill that strengthens your ability to lead, connect, and thrive. Whether you are a professional navigating complex teams, a student building self-confidence, or an individual seeking inner balance — mastering emotional intelligence empowers you to make thoughtful decisions guided by awareness, empathy, and purpose.
By embracing the five elements and four pillars of emotional intelligence, and by practicing emotional mastery daily, you create not just success — but a life defined by emotional clarity, connection, and resilience.