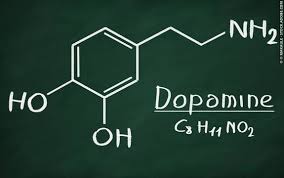
Introduction: What Is Dopamine and Why It Matters
Dopamine is often called the brain’s “feel-good” or “motivation” chemical — and for good reason. It plays a vital role in how we feel pleasure, stay focused, make decisions, and even move our bodies. Every time you accomplish something, enjoy your favorite food, or receive praise, your brain rewards you with a burst of dopamine.
This powerful neurotransmitter influences motivation, learning, mood, and habit formation. It’s not just about happiness — it’s about drive. Without balanced dopamine levels, you might struggle with concentration, low energy, or a lack of enthusiasm. Too much, on the other hand, can lead to impulsivity or even certain mental health disorders.
Understanding dopamine gives us a deeper look into how our mind, body, and behavior are connected. It’s the biological bridge between our goals and actions, and mastering its balance can lead to better emotional well-being, productivity, and overall life satisfaction.
The Science of Dopamine: How It Works in the Brain
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. It is produced in several areas of the brain, mainly the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These regions are part of the dopaminergic pathways, which influence movement, emotion, and reward processing.
There are four main dopamine pathways in the brain:
- Mesolimbic Pathway: Known as the reward pathway, it’s activated during pleasurable experiences like eating, exercising, or achieving goals.
- Mesocortical Pathway: Involved in cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and problem-solving.
- Nigrostriatal Pathway: Controls movement and coordination — dysfunction here is linked to Parkinson’s disease.
- Tuberoinfundibular Pathway: Regulates hormone secretion, particularly from the pituitary gland.
Dopamine works by binding to dopamine receptors (D1–D5), which are spread throughout the brain. Once released, it influences how we respond to pleasure, rewards, and motivation. After completing its job, dopamine is either recycled (reuptake) or broken down by enzymes such as MAO (monoamine oxidase).
The fascinating part? Dopamine is not just about pleasure — it’s about anticipation. Studies show dopamine spikes not when you receive a reward, but when you expect one. This means dopamine motivates you to take action to achieve goals, rather than just feeling good afterward.
Can You Increase Dopamine Naturally?
Yes — and in fact, the healthiest and most sustainable way to boost dopamine is through natural lifestyle habits. Artificial stimulants like drugs or excessive caffeine can spike dopamine temporarily but lead to long-term depletion. Instead, you can enhance dopamine naturally through simple, daily choices.
1. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is one of the most powerful dopamine boosters. Exercise increases dopamine receptor sensitivity, improves blood flow to the brain, and releases endorphins. Activities like running, cycling, or even walking can elevate dopamine levels for hours after a workout.
2. Eat Dopamine-Boosting Foods
Dopamine is synthesized from an amino acid called tyrosine, which is found in protein-rich foods. Include:
- Lean meats, fish, and eggs
- Nuts and seeds (especially almonds and pumpkin seeds)
- Dairy products
- Bananas, avocados, and beets
These foods provide the raw materials your body needs to produce dopamine naturally.
3. Get Enough Sleep
Dopamine levels naturally rise in the morning to make you feel alert and decrease at night to help you rest. Sleep deprivation disrupts this rhythm, reducing dopamine receptor sensitivity. Prioritizing 7–9 hours of quality sleep keeps dopamine in balance.
4. Practice Gratitude and Mindfulness
Psychological well-being strongly affects dopamine. Gratitude exercises, meditation, and mindfulness increase baseline dopamine levels by promoting positivity and lowering stress hormones like cortisol.
5. Listen to Music You Love
Music activates the brain’s reward pathways, causing a dopamine surge similar to eating or accomplishing something meaningful. Even anticipating your favorite part of a song boosts dopamine.
6. Set and Achieve Small Goals
Each time you complete a task — no matter how small — dopamine is released. This is why checking items off a to-do list feels satisfying. Setting daily achievable goals helps sustain dopamine naturally.
What Are the Symptoms of Low Dopamine?
Low dopamine levels can have a significant impact on your mental and physical health. Because dopamine influences mood, energy, motivation, and pleasure, its deficiency can mimic symptoms of depression, fatigue, or even certain neurological disorders.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Persistent fatigue or lack of energy
- Difficulty focusing or completing tasks
- Loss of interest in pleasurable activities
- Low mood, sadness, or emotional numbness
- Poor motivation or apathy
- Cravings for sugar, caffeine, or addictive substances
- Sleep disturbances
- Reduced libido
In severe cases, low dopamine is linked to conditions such as:
- Parkinson’s disease (due to dopamine cell loss in the brain)
- ADHD (attention dysregulation and reward processing issues)
- Depression and anhedonia (inability to feel pleasure)
If you experience multiple symptoms consistently, it may indicate dopamine dysregulation — where your brain’s reward system is not functioning optimally.
What Depletes Dopamine the Most?
Modern lifestyles can unknowingly drain dopamine. Certain behaviors and substances create a quick rush of dopamine, followed by a crash, leading to long-term depletion and reduced receptor sensitivity.
1. Chronic Stress
Stress increases cortisol, which directly interferes with dopamine production and receptor function. Over time, chronic stress blunts the brain’s reward system, making joy harder to experience.
2. Poor Diet
Highly processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats reduce dopamine synthesis. Diets low in tyrosine or essential vitamins like B6, folate, and iron also limit dopamine production.
3. Lack of Sleep
Sleep deprivation lowers dopamine receptor availability, leaving you sluggish and demotivated. It also disrupts circadian rhythms that regulate dopamine release.
4. Substance Abuse
Drugs like cocaine, methamphetamine, and even nicotine create unnatural dopamine surges. Repeated use overstimulates and eventually desensitizes dopamine receptors, leading to addiction and emotional flatness.
5. Digital Overstimulation
Constant social media scrolling, gaming, or binge-watching floods your brain with mini dopamine hits. This trains your brain to crave constant stimulation and weakens its response to real-life rewards.
6. Sedentary Lifestyle
Physical inactivity slows blood flow to dopamine-producing areas of the brain. Regular movement helps keep dopamine active and balanced.
7. Neglecting Mental Health
Unresolved emotional issues or trauma can chronically suppress dopamine. Practices like therapy, journaling, and mindfulness help restore mental and emotional balance.
What Is the Difference Between Dopamine and Serotonin?
Dopamine and serotonin are both vital neurotransmitters, but they serve distinct roles in the brain.
| Feature | Dopamine | Serotonin |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Motivation, reward, and goal-seeking behavior | Mood stabilization, calmness, and well-being |
| Main Brain Pathways | Reward and pleasure circuits | Mood regulation and sleep control |
| Effect on Behavior | Drives focus, ambition, and anticipation | Creates balance, satisfaction, and peace |
| Deficiency Effects | Apathy, fatigue, depression, addiction | Anxiety, irritability, mood swings |
| Chemical Relationship | Works with adrenaline and norepinephrine | Works with melatonin and oxytocin |
Think of dopamine as the “go-getter” — it drives you toward goals, excitement, and reward. Serotonin, on the other hand, is the “stabilizer” — it helps you feel content, calm, and emotionally balanced. Both must work together for optimal mental health. Too much dopamine can lead to impulsivity, while too little serotonin can cause anxiety and sadness.
How Dopamine Influences Motivation, Focus, and Happiness
Dopamine is the biological foundation of motivation and reward-seeking behavior. When you set a goal, your brain anticipates the reward and releases dopamine — this anticipation energizes you to act.
Motivation
The mesolimbic dopamine pathway fuels goal-directed behavior. When dopamine is high, you feel driven and energized. Low dopamine makes even small tasks feel overwhelming.
Focus and Productivity
Dopamine enhances prefrontal cortex activity, improving concentration, decision-making, and problem-solving. Balanced dopamine keeps your attention sharp and helps you resist distractions.
Happiness and Reward
While serotonin gives long-term emotional stability, dopamine provides short bursts of pleasure and excitement. This chemical dance creates the feeling of joy when you achieve something meaningful.
However, it’s essential to balance dopamine levels. Constant chasing of pleasure (through screens, junk food, or validation) can lead to dopamine burnout, leaving you unmotivated and emotionally flat.
Lifestyle Habits to Maintain Healthy Dopamine Levels
Maintaining balanced dopamine doesn’t require extreme measures — it’s about consistent, brain-friendly habits that promote emotional stability and motivation.
1. Balanced Nutrition
- Eat foods rich in tyrosine and vitamin B6, essential for dopamine synthesis.
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods.
- Include omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseeds, walnuts) to support brain health.
2. Consistent Physical Activity
Aerobic exercises like running, dancing, or swimming enhance dopamine receptor sensitivity. Even light activities such as yoga or stretching help regulate mood.
3. Prioritize Sleep
Stick to a regular sleep schedule. Quality rest allows the brain to reset dopamine receptors and restore energy.
4. Social Connections
Healthy relationships trigger dopamine through social bonding and laughter. Human interaction is a natural reward system that boosts both dopamine and serotonin.
5. Mindful Living
Meditation, gratitude journaling, and mindful breathing reduce stress and stimulate dopamine production naturally.
6. Avoid Overstimulation
Take digital detox breaks. Limiting social media and screen time helps reset dopamine sensitivity and restores motivation.
The Role of Diet, Sleep, and Exercise in Dopamine Regulation
Diet
Nutrients directly influence dopamine production. Tyrosine (found in protein) converts to L-DOPA, the immediate precursor of dopamine. Vitamins B6, B9, and C act as cofactors in this conversion process. Iron and magnesium also play key roles.
A deficiency in these nutrients can slow dopamine synthesis. Eating a diverse, whole-food diet ensures your brain has all the ingredients needed for stable dopamine function.
Sleep
Sleep helps regulate dopamine receptors. Poor sleep reduces receptor sensitivity, leaving you feeling mentally foggy and unmotivated. Establishing a consistent sleep routine enhances morning dopamine surges, improving alertness and drive.
Exercise
Exercise increases dopamine both directly and indirectly. It stimulates production, enhances receptor sensitivity, and releases endorphins that synergize with dopamine’s effects. Consistent movement keeps the reward system healthy and balanced.
Dopamine and Mental Health: Understanding Its Link with Anxiety, Depression, and Addiction
Depression
Low dopamine levels are associated with feelings of apathy, hopelessness, and an inability to experience pleasure (anhedonia). Many antidepressants target dopamine pathways to restore motivation and emotional vitality.
Anxiety
Although primarily linked to serotonin, anxiety can be worsened by dopamine imbalances. Overactive dopamine circuits can heighten alertness, causing restlessness and overthinking.
Addiction
Addictive substances and behaviors hijack the brain’s reward system by flooding it with dopamine. Over time, the brain compensates by reducing receptor sensitivity, making it harder to feel pleasure naturally. This leads to cravings and dependence.
ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is strongly tied to dopamine dysregulation. Medications for ADHD often increase dopamine availability to improve focus and impulse control.
Conclusion: Balancing Dopamine for a Healthier Mind and Life
Dopamine is much more than a pleasure chemical — it’s the core of motivation, learning, and emotional balance. It drives us to set goals, learn from experience, and find satisfaction in achievement. But balance is key.
Too little dopamine drains energy and joy, while too much can lead to impulsivity and burnout. The best way to sustain healthy levels is through natural living: good sleep, regular exercise, nutritious food, mindfulness, and meaningful relationships.
By understanding dopamine, we gain insight into one of the brain’s most powerful systems — one that governs our drive, focus, and happiness. When we nurture it wisely, we create the foundation for lasting motivation, inner peace, and a thriving mind.