Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that affects many men, and while it is often linked to physical health issues like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or hormonal imbalances, psychological factors can also play a significant role in its development.
If you find that your erectile dysfunction is related to emotional, psychological, or physical causes, rest assured that you’re not alone– and there are various effective treatment options available. Understanding the psychological and physical reasons behind ED is the first step toward overcoming it, and addressing these underlying issues can significantly improve both your sexual health and overall well-being
Psychological Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can stem from a variety of psychological factors that interfere with sexual arousal and performance. Some of the most common psychological causes include:

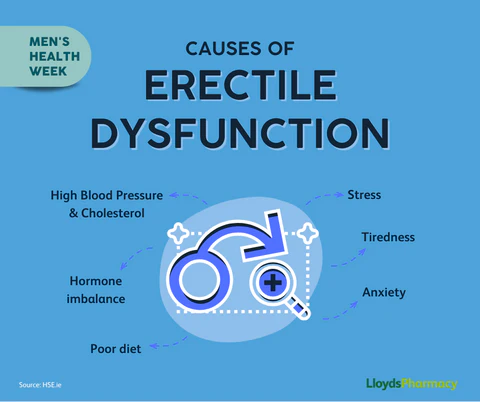
Stress and Anxiety: Everyday stressors, whether related to work, family, or financial pressures, can lead to an overactive stress response, raising levels of cortisol and other stress hormones. This can disrupt your ability to relax and affect your sexual performance. Additionally, anxiety about sexual performance itself– often referred to as performance anxiety– can create a vicious cycle, where fear of failure leads to further erectile difficulties.
Depression: Depression can diminish libido, decrease motivation, and lead to feelings of hopelessness. The emotional and mental fatigue associated with depression often makes it challenging for men to feel motivated or excited about sex, leading to difficulty maintaining an erection.
Relationship Issues: Problems in your relationship– whether emotional disconnect, unresolved conflicts, lack of intimacy, or poor communication– can contribute to psychological ED. When a relationship is strained, feelings of frustration or dissatisfaction can manifest as sexual difficulties.
Low Self-Esteem and Body Image Issues: Men who struggle with their self-image or feel inadequate in their sexual abilities may experience performance anxiety or a loss of confidence. This often leads to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Guilt and Shame: Feelings of guilt or shame about past sexual experiences or cultural and religious beliefs around sex can create mental barriers to sexual arousal and performance.
Sexual Trauma or Abuse: Past experiences of sexual trauma or abuse can lead to emotional scars that interfere with sexual health. These traumas may cause anxiety, trust issues, or a general sense of disconnection from one’s sexual self.
Physical or Internal Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
While psychological factors are a common cause of ED, physical and internal health issues can also contribute to erectile difficulties. Here are some of the most common physical causes:
Cardiovascular Disease: Conditions such as atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries) or heart disease can restrict blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. As blood vessels become less flexible, the flow of blood necessary for an erection is impaired.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, which are essential for normal sexual function. Men with diabetes may experience reduced sensation, nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy), or poor blood flow, all of which can contribute to ED.
Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone levels or other hormonal issues, such as thyroid problems, can affect libido and sexual function. Testosterone plays a critical role in sexual arousal, and any disruption in its balance can lead to ED.
Neurological Disorders: Conditions that affect the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, or spinal cord injuries, can disrupt the nerve signals required for an erection. Nerve damage from surgery or injury can also be a contributing factor.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Excess weight and lack of physical activity are closely linked to erectile dysfunction. Obesity can affect hormone levels, cause insulin resistance, and reduce blood flow– all of which can contribute to ED. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can significantly reduce the risk of developing ED.
Medication Side Effects: Some medications, including antidepressants, antihypertensives (for high blood pressure), and certain medications for prostate conditions, may have side effects that interfere with sexual function. If you suspect your medication is contributing to ED, speak with your doctor about alternatives or adjustments.
Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Use: Smoking damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis, while excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the brain’s ability to signal arousal. Both habits can contribute to erectile difficulties over time.
Pelvic Surgery or Injury: Surgery or injury to the pelvic region, such as prostate surgery, can cause nerve or tissue damage, leading to ED. The pelvic floor muscles and nerves play an important role in sexual function, and any damage to these structures can interfere with the ability to maintain an erection.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction Due to Psychological and Physical Causes
Whether ED is caused by psychological or physical factors, treatment is available. In many cases, addressing both the mental and physical aspects of ED is necessary to achieve the best results. The following treatment options can help men overcome psychological and physical ED:
- Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy).
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps men identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. By addressing the root causes of mental health issues, CBT can reduce performance anxiety and build confidence, making it easier to engage in sexual activity without fear of failure.
Sex Therapy: For men whose ED is caused by relationship issues or poor communication, sex therapy can help improve intimacy, rebuild emotional connections, and enhance sexual satisfaction.
- Medical Treatment.
Medications: For physical causes of ED, medications like Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), or Levitra (vardenafil) can help improve blood flow to the penis. These medications are effective for many men, though they are typically used in conjunction with lifestyle changes for optimal results.
Hormonal Therapy: If low testosterone or another hormonal imbalance is the cause of ED, hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed. This can help restore testosterone levels and improve sexual function.
Penile Injections or Vacuum Devices: In some cases, injections of medications like alprostadil can help induce an erection. Vacuum devices can also be used to create a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into the area and helping to maintain an erection.
- Lifestyle Changes.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve circulation, reduce stress, and enhance overall health, which can help alleviate both psychological and physical causes of ED.
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support heart health, blood flow, and hormone regulation, all of which are important for sexual function.
Quitting Smoking and Limiting Alcohol: Stopping smoking and moderating alcohol intake can help improve circulation and reduce the risk of ED caused by vascular issues or nerve damage.
- Supportive Therapies.
Couples Counseling: If relationship difficulties are contributing to ED, couples counseling can help improve communication, reduce stress, and strengthen intimacy.
Stress Management: Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety, improving both mental and physical sexual health.
Conclusion.
Erectile dysfunction caused by psychological or physical factors is a common issue that many men face, but it is highly treatable. Whether stress, anxiety, depression, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or other factors are at the root of your ED, there are numerous effective therapies and lifestyle changes that can help you regain confidence, reduce anxiety, and improve your sexual health.
Seeking help from a healthcare provider, therapist, or counselor is a crucial step toward overcoming ED and improving your quality of life. By addressing both mental and physical aspects of ED, you can pave the way for a healthier and more fulfilling sexual life.



