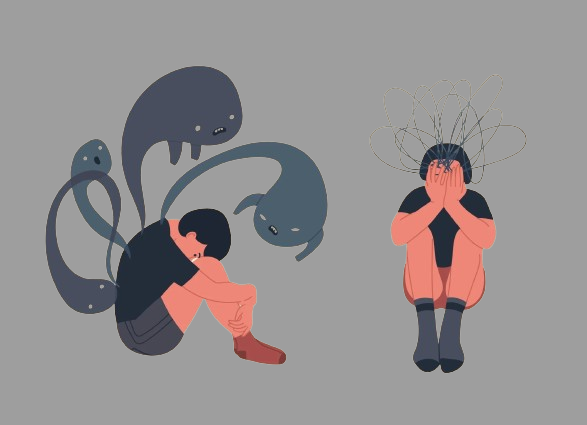
People sometimes refer to broad sensations of trepidation, uneasiness, or worry as “anxiety.” But experiencing anxiety is not the same as having an anxiety condition.
While having anxiety is common during stressful moments in life, if your anxiety is ongoing and interfering with your day-to-day activities, you may be suffering from an anxiety disorder.1.
Anxiety is usually treated or controllable with a range of short- and long-term interventions, however it can be crippling for others. This article will offer various strategies for dealing and overcoming anxiety.
What is Anxiety disorder?
Among the several mental health conditions is anxiety disorder. You could react with fear and dread to specific things and circumstances if you suffer from an anxiety condition. Additionally, you can exhibit bodily symptoms of anxiousness including perspiration and a racing heart.

A certain level of anxiousness is normal. If you have to make a big decision, go on an interview, take an exam, or deal with a situation at work, you could feel worried or anxious. Anxiety may even be advantageous. Anxiety, for instance, helps us focus our attention and identify potentially dangerous circumstances, keeping us safe.
Signs and symptoms
Depending on the kind of anxiety condition you have, there are different symptoms. The following are typical signs of an anxiety disorder:
Physical signs and symptoms:
- Hands that are either cold or sweaty.
- Mouth feeling parched.
- Palpitations in the heart.
- Nausea.
- Hands or feet numbness or tingling.
- Tense muscles.
- Breathlessness.
Mental signs and symptoms

- experiencing panic,
- dread,
- and unease.
- Nightmares.
- recurring memories or
- Flashbacks to tragic events.
- erratic,
- Compulsive thoughts.
Symptoms of behavior:
- Unable to be silent and composed.
- Ritualistic actions, such frequently washing your hands.
- Difficulty falling asleep.
Causes of anxiety
Anxiety disorders are similar to other mental health conditions. They are not the result of character defects, personal weakness, or issues with upbringing. However, the precise source of anxiety disorders is unknown to researchers. They believe that a number of variables are involved:
Trauma in childhood

Neglect or physical, emotional, or sexual abuse throughout childhood can have a lasting impact on a person’s mental health. Those who have experienced trauma as children may be more prone to anxiety. This may be the result of modifications to brain development that impact memory, mood management, and our fight-or-flight response.
Negative ideas about oneself or the outside world resulting from childhood trauma can also make it harder to handle stressful situations and raise the risk of anxiety.
Social seclusion
When compared to people who report having positive social ties, those who suffer social isolation or loneliness frequently have fewer or lower-quality social contacts. Social isolation can make it difficult to strike up conversations with people, which frequently results in feelings of uneasiness and rejection.
In a similar vein, loneliness can exacerbate anxiety by fostering low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy. Although loneliness can impact everyone, there are risk factors that raise our chances of experiencing severe and long-lasting loneliness, which can have an adverse effect on our mental health and occasionally raise our anxiety levels. Among them are:
- Loss of a spouse
- Being unmarried and jobless
- Living by Oneself
- Possessing a chronic illness or disability
- being in the age range of 16 to 24
- Also Being a caregiver and a member of an ethnic minority
- Being Gay and Positive
Negative incidents in life
Unfavorable experiences in life can also exacerbate anxiety. These are the kinds of things that upset our sense of security or wellbeing and have a profound emotional impact.
Unfavorable life experiences that can cause anxiety in certain individuals include:
- Divorce or the breakdown of a meaningful relationship can make someone feel scared and vulnerable.
- Abuse or domestic violence experience that leaves you fearful and intimidated to live in your own house, which is supposed to be a safe place.
- Exposure to demanding work, learning, or social contexts; for instance, being the target of bullying, harassment, or discrimination in any of these settings, which can cause persistent anxiety (especially in the case of women and marginalized communities).
Lack assistance for mental health
Unequal access to resources and support for mental health can be caused by a variety of circumstances. Waiting periods, transportation, education and literacy, language or cultural hurdles, discrimination, stigma, and prejudice are a few typical obstacles. Anxiety might increase when people are unable to get the appropriate support when they need it.
How to deal with Anxiety: 5 Techniques to Use
The symptoms of anxiety can be upsetting and have a negative effect on your life. There are numerous self-help methods for managing anxiety, even though each person’s needs will vary in terms of therapy.

Analyze Your Thought Process
Anxiety frequently results in uncontrollably obtrusive, upsetting images and troubling thoughts. Identifying negative thought patterns and substituting them with constructive ideas or thoughts is one strategy to break the cycle of negative thinking. Any positive vision has the power to lessen tension; it is not necessary for these images to be connected to the troubling circumstance.2.
Another thing you could attempt is doubting the accuracy of your ideas. Avoid concentrating on things that are unhelpful or untrue. As soon as you catch yourself thinking something cruel or false, stop and shift your focus to something more constructive.
Deep breathing
One useful strategy for reducing anxiety symptoms in the moment is intentional breathing. Deep breathing techniques can be twice as beneficial because they both promote relaxation, which reduces stress in the body, and work as a diversion when employed as a focus point to break the cycle of bothersome thoughts.2.
Deep breathing exercises come in a variety of forms. Try this one, which is known as 4-7-8 breathing

- Choose a comfortable position and consciously let your muscles relax.
- Shut your eyes or avert your focus.
- Count to four while you inhale deeply and let your tummy expand.
- Breathe out slowly and count to seven.
- Breathe out, tense your abdomen, and count to eight.
- Go on for however long you’d like.
Grounding Methods
Exercises that ground or “earth” the body help it become more connected to the outside world. Stabilizing factors like grounding can help with heart rate slowing, stress and anxiety reduction, and better sleep. Spending time in the grass, dirt, and other natural settings outside is the most straightforward method to learn grounding.
Try going barefoot or taking off your shoes to experience grounding, which works best when your skin makes direct contact with the Earth’s surface.
When it’s unsafe or impractical to spend time outside, special equipment can also be utilized for grounding.
Exercise / Work out
Movement and physical activity are associated with improved mental health and a decrease in symptoms of anxiety. All movements that are structured, regular, and meant to promote health are considered forms of exercise. While the effects of exercise on different types of anxiety may vary, most exercises are beneficial in reducing symptoms, particularly when combined with other treatments such as counseling and medication.4
Here are a few workout examples you can try:

- Exercises involving the heart, like riding, walking, hiking, or swimming
- Weight-bearing workouts include push-ups, squats, and weightlifting
- stretching techniques including tai chi, yoga, and Pilates
Before beginning a new fitness regimen, make sure to consult a healthcare professional.
Using aromatherapy
Using essential oils to enhance health and relaxation is known as aromatherapy. Different oils can be ingested, applied topically, added to compresses, inhaled, and used in baths. Certain essential oils have been demonstrated to lessen anxiety. Essential oils have long been utilized as an alternative form of medication. Among them are:
- Rosemary oil
- Lavender
- Bergamot
- Lemon
- Orange
You may buy aromatherapy oils for usage at home over the counter. Make sure you understand the proper application of aromatherapy before using it, and never ingest an oil without first making sure it’s safe to do so. Speak with an aroma therapist for professional assistance on utilizing aromatherapy. They can help you choose which oils are best for your symptoms and provide tips on how to use them.