Feeling anxiety after eating lion’s mane mushrooms? This article examines the less well-known side effects of Lion’s Mane, investigates potential causes, and provides pain management techniques.
The lion’s mane mushroom, or Hericiumerinaceus, has become more well-known due to its possible advantages for general mental health and cognitive function. But some people claim to feel anxious after eating foods or pills made with this unusual fungus called Lion’s Mane. The consequences of the mushroom on mental health are a significant topic that is brought up by this unanticipated reaction.
What is lion’s mane mushroom?
Large, white mushrooms that resemble a lion’s mane are known as lion’s mane mushrooms. There are actually three distinct species of mushrooms, despite the fact that they are usually considered to be one kind. It is Hericium erinaceus that is most commonly available.
Generally resembling white pom-poms, lion’s mane mushrooms have culinary and medicinal uses. Asian nations including China, Japan, Korea, and India use them widely.
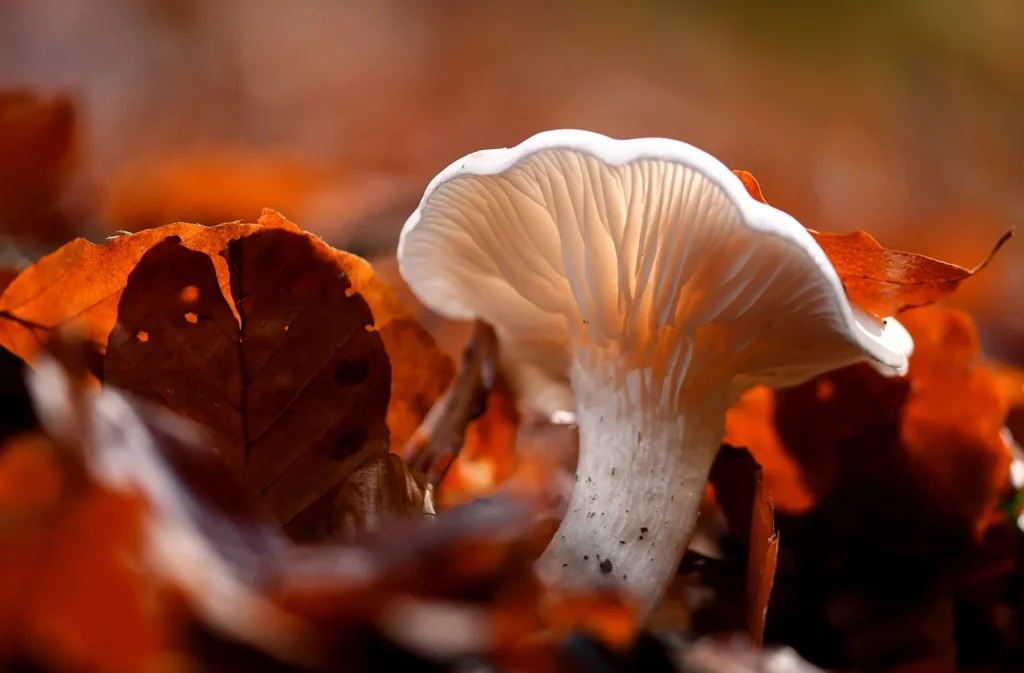

Lion’s mane mushrooms are available in health food stores, eateries, and supplement stores. Many people compare the flavor of lion’s mane mushrooms to fish. They can be cooked, dried, or eaten raw. The mushroom is available in liquid, pill, and powder form as a dietary supplement.
Rich in vitamins including thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin are lion’s mane mushrooms. They are also a good source of potassium, zinc, and manganese, among other important minerals.
Possible Causes of Anxiety Caused by Lion’s Mane
these are the following possible causes of anxiety caused by lion’s mane:
Sensitivity in Individuals
The effects of Lion’s Mane may affect some people more than others, just as some people are more sensitive to particular foods or drugs. This increased sensitivity may cause uneasiness or trepidation.
Quantity
The amount of Lion’s Mane taken might be very important. While some people may be more sensitive to even ordinary amounts, others may develop anxiety while taking higher-than-recommended doses.
Neurotransmitter Interaction
The way that Lion’s Mane affects neurotransmitter pathways may be a factor in anxiety in certain people. Although studies are ongoing, it’s plausible that the mushroom’s effects on brain chemistry could make sensitive people feel uneasy.
Background Anxiety
Any chemical that affects brain function, such as Lion’s Mane, may make anxiety more likely to occur in people with a history of anxiety problems.
Benefits of lion’s mane
Thus far, the majority of scientific investigation on lion’s mane and its effects has been conducted on animals, in test tubes, and in tiny clinical trials. To fully comprehend the mechanisms of action and potential benefits and drawbacks of this substance in the body, more research is required. However, some evidence suggests that there may be advantages.

Brain Activity
Cognitive function is one area where lion’s mane has demonstrated promise. For instance, in a 2023 study, it improved memory and brain cell proliferation in the brains of mice. Similarly, a brief investigation of the mushroom’s effects on young people’ moods and cognitive performance suggested less stress and quicker processing times. The hypothesis that lion’s mane could improve brain function is supported by numerous previous investigations.
Similarly, a tiny 2009 study found that lion’s mane may help elderly persons with minor cognitive impairment. For 16 weeks, 30 older persons with mild cognitive impairment were randomly randomized to receive either lion’s mane extract or a placebo daily.
Combating free radicals and inflammation
Free radicals, which are unstable molecules found in our bodies, are linked to a number of health issues, such as cancer, arthritis, and heart disease. The compounds found in lion’s mane mushrooms have the potential to be very strong antioxidants, which prevent free radical damage. They also include anti-inflammatory compounds that, according to research on animals, appear promising.
Combating brain disorders such as dementia
Lion’s mane mushrooms may have a part in the prevention or treatment of cognitive decline, including Alzheimer’s disease, according to certain animal research and limited, preliminary human investigations.
For instance, those who took tablets containing powdered Hericium erinaceus for four months shown a transient improvement on cognitive tests in a trial including thirty older adults with mild cognitive impairment. In mice, the mushrooms have also been demonstrated to reduce Alzheimer’s symptoms and disease-related brain alterations.
Lowering depression and anxiety
Extracts from lions’ manes may be able to treat certain mental health issues. A study was conducted on Japanese women with various health issues, such as menopausal symptoms and sleep disorders, to investigate this potential. For four weeks, some received cookies containing extracts from lion’s mane, while others received placebo cookies.
In comparison to the placebo group, the ladies who received the lion’s mane cookies reported reduced levels of stress and depressed symptoms.
Researchers think that the two types of compounds found in lion’s mane mushrooms, erinacines and hericenones, may be in charge of any antidepressant effects. The release of nerve growth factor (NGF), a molecule that controls brain cell development and survival, is impacted by these substances. It’s possible that traditional antidepressants function by altering NGF levels.
Side effects of lion’s mane
The safety of eating or taking lion’s mane supplements over an extended length of time, as well as any potential negative consequences, are not well studied topics.
There have been reports of potential allergic reactions to lion’s mane mushrooms. One man experienced respiratory difficulties. In another, a man got a large rash that cleared up after he stopped consuming the mushrooms. Before using lion’s mane mushrooms in your diet or taking them as a supplement, consult your doctor if you have a history of allergies, asthma, or any other medical issue.
Certain mushroom supplement labels advise against using them if you are expecting a baby, are nursing a baby, or are contemplating surgery. Many kinds of mushrooms have been linked to adverse effects such as headaches, gastrointestinal (GI) pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, disorientation, skin sensitivity, and allergic responses.
Lion’s mane Supplements
Numerous supplements with lion’s mane mushrooms are available for purchase. Notwithstanding the numerous health advantages listed on supplement labels, dietary supplements in the US are not subject to the FDA’s review procedure, which verifies the efficacy and safety of pharmaceuticals. No matter what kind of mushroom, there hasn’t been the kind of thorough research done to determine if they are safe and beneficial for treating any particular ailment.

The manufacturer of a lion’s mane supplement has received warnings from the FDA in at least one instance to cease promoting it as “great for brain injury recovery” and as able to “reduce symptoms of anxiety & depression.”
Powdered lion’s mane mushroom
Supplements containing lion’s mane can be found in a variety of forms, such as powders that are created by pulverizing the mycelium (the root) or the fruiting body, the mushroom head. You can get it in capsule form or as loose powder to mix into meals or drinks. Liquid extracts are also available; these are typically produced by boiling the fruiting body in either water or alcohol.
Dosage
There is no recommended dosage for lion’s mane mushrooms because they haven’t been thoroughly studied in humans. Various quantities have been employed in various investigations. In one study, for instance, older persons with mild cognitive impairment consumed 250 mg, or less than 1 gram, of mushroom powder three times a day. Women experiencing menopausal symptoms took two grams daily in another trial. One study that looked at the effects of 500 milligrams, three times a day, or 1.5 grams, on mood and sleep in obese individuals employed this dosage.
In terms of components and potency, products available in stores and online may vary not just from those used in scientific studies but also from one another. Follow the directions on the label at all times.