Drug addiction has historically been stigmatized and linked to moral failings and poor judgment. In actuality, substance addiction can strike people from many walks of life for no apparent reason. Because of the powerful effects that most drugs have on the brain and body, they are intrinsically addicted both physically and intellectually. We are predisposed to desire to repeat the behavior because of the way some substances affect the brain’s reward and pleasure centers. The most addictive medications have the potential to be lethal when used repeatedly and to cause permanent harm.
What is drug addiction?
Substance use disorder, another name for drug addiction, is a brain and behavioral illness that makes it difficult for a person to regulate their use of drugs or medications, whether they are legal or not. Drugs also include substances like nicotine, alcohol, and (cannabis) marijuana. When you have an addiction, you could keep using the drug even though it hurts you.
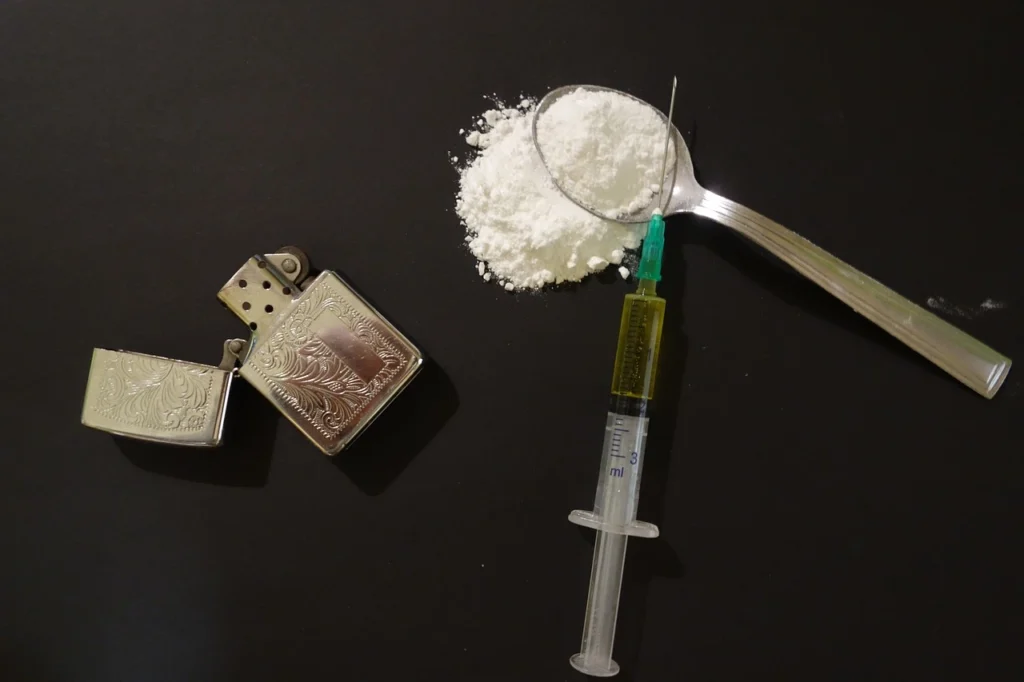

Drug addiction can begin with experimenting with recreational drug use in social settings, and for some users, this can lead to increased drug usage frequency. For some people, especially those who use opioids, drug addiction starts when they consume prescription medications or get them from someone else who has a prescription.
Each substance has a different risk of addiction and a different rate of addiction onset. Certain medications carry a greater risk and lead to addiction more quickly than others, such as opioid painkillers.
You might eventually require higher dosages of the substance to feel euphoric. Also you might soon find that you need the medicine to feel well. You could find that it gets harder and harder to stop using drugs as your usage grows. When trying to quit using drugs, you could experience severe cravings and become physically sick. We term these signs of withdrawal.
These are the top 10 most addictive drugs are following
The top 10 most addictive drugs
1. Heroin
Morphine is the base for the opiate substance heroin. It is possible to inject, snort, or smoke this extremely addictive substance. Heroin is typically discovered as a white or brown powder along with a sticky black material called “black tar.” In particular, the main ingredient in opium, morphine, is used to make heroin. The naturally occurring material known as opium is taken from the opium poppy’s seedpod. An alarming pandemic of heroin addiction and other opioid drug addiction—including prescription opioids—is presently plaguing the United States. Over 136 Americans lose their lives to opioids, including heroin, each day.
2. Cocaine
The white, powdery medication is a stimulant derived from coca leaves and is usually taken via the nose. Drug traffickers frequently combine it with other materials like flour, talc, or cornstarch to boost earnings. Additionally, cutting cocaine with other narcotics like fentanyl is a typical practice among sellers, which significantly raises the risk of overdosing. When cocaine is used frequently, it disrupts normal nerve cell communication by raising dopamine levels in the brain. This implies that dopamine sensitivity decreases in the brain, necessitating higher dosages for users to experience happiness. Depression, tiredness, sluggish thinking, and nightmares and insomnia are common withdrawal symptoms. Snorting cocaine can cause runny nose, nosebleeds, loss of smell, and difficulty swallowing.

3. Crack cocaine
Cocaine that has been processed into the shape of a rock is known as crack cocaine. To get a high, people smoke the substance. Similar to its derivative, crack cocaine is highly powerful and produces a strong high that wears off more quickly. Because the chemical high wears off faster than cocaine (generally in approximately 10 minutes), addicts usually look for higher and more frequent dosages to get the same feeling. Coming down from crack produces the opposite feelings of exhilaration, vigor, and enjoyment that one experiences while high.
4. Alcohol
Although many people do not view alcohol as a drug, alcohol addiction is a very frequent disorder. Alcohol is a commonly accessible and lawful substance. Like other drugs, alcohol acts on the brain by releasing dopamine. Because it tends to reduce anxiety, which relaxes people in social circumstances, it is frequently referred to as the “social drug.” When someone depends on alcohol to help them release endorphins, their usage of the drug can easily get out of hand. It is crucial that those who are addicted to alcohol seek treatment for their illness because drinking can also result in severe withdrawal symptoms.
5. Fentanyl
Fentanyl, which is not to be confused with heroin, has gained notoriety as the synthetic (false, man-made) form of the drug. More American youth deaths have been caused by illicit fentanyl than by heroin, meth, cocaine, benzos, and prescription drugs put together. It is the primary factor contributing to the rise in overdose deaths in the country. Most illegal fentanyl is produced in China and enters the country through the border between Mexico and the United States. Before being sold, distributors and dealers “cut” fentanyl that has been smuggled into huge batches; this results in an uneven fentanyl to cutting agent ratio and increases the possibility of “deadly batches.”
6. Barbiturates
In the past, doctors would frequently prescribe barbiturates, a class of prescription medication, to treat ailments like anxiety. Although they are administered significantly less frequently than they formerly were because of their addictive characteristics, these depressants can also be used to treat epilepsy. Barbiturates are very addicting and are sold illegally on the streets. Known by many as “downers,” these substances work against the effects of stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamines. The symptoms of withdrawal from these substances are comparable to those of alcohol withdrawal and can be quite dangerous.
7. Methadone
One drug that is frequently used to treat heroin addiction is methadone. But this medicine alone has the potential to be extremely addictive. This is why the patient needs to be closely observed in a medical setting whenever the medicine is given to lessen withdrawal symptoms. In order to lessen the symptoms of withdrawal and prevent developing a secondary addiction to methadone, dosages should be gradually decreased. Not to mention, alternative medications like Vivitrol and Suboxone don’t have many of the side effects of methadone, making them suitable for medication assisted treatment.

8. Crystal meth
Methamphetamine comes in the form of crystal meth. All of these medications are manufactured by humans and are quite dangerous. All forms of meth are stimulants, but crystal meth is thought to be the strongest and riskiest. Although it can also be injected or inhaled, smoking crystal rock is the usual method. This dangerous substance produces a strong euphoric high. It can improve focus and cause pleasure and excitability. At higher dosages, it can also cause psychosis and violent or aggressive behavior. The substance has a strong addictive potential. Because of the increased dopamine and norepinephrine it produces, the brain becomes dependent on it. This also gradually reduces the brain’s capacity to create these substances naturally.
9. Amphetamines
Amphetamines are stimulants, just like methamphetamine, which is produced illegally. These medications are, nevertheless, legally prescribed and used to treat common conditions including ADHD and ADD. One such variant that has also been sold illegally on the streets is Adderall. Amphetamines can have a number of negative consequences in addition to being highly addictive when used over their recommended dosage. These may consist of, but are not restricted to:
- Speaking with difficulty
- mouth dryness
- Constipation
- difficulty falling asleep
- lightheadedness
- cardiac issues
10. Benzodiazepines
Some of the most often prescribed drugs in the US are benzodiazepines, or “Benzos,” which help patients sleep, relax their muscles, and lessen anxiety and seizures. Due to their addictive qualities, they are also frequently abused, with a dependence score of 1.83. Benzos include medications like Restoril, Valium, and Xanax. After stopping Benzos, users may begin to experience anxiety and insomnia one to four days later. After that, among a plethora of unpleasant effects, those who stop taking the medication for the next 10 to 14 days may endure panic attacks, insomnia, nausea, dry retching, migraines, and stiffness and discomfort in their muscles. Because benzo withdrawal can be lethal in some situations, detoxification under medical supervision is required.
Signs and symptoms

Among the signs or behaviors of drug addiction are:
- having strong cravings for the substance that keep you from thinking about anything else and making you feel as though you have to use it frequently—
- daily or perhaps multiple times a day
- gradually requiring more medication to achieve the same result
- taking the medication for longer than you had meant to and in bigger doses
- ensuring that you keep the medication on hand
- spending money on drugs despite not being able to afford them
- Cutting back on social or recreational activities or failing to fulfill commitments and work responsibilities due to drug usage
- staying on the medication despite knowing that it’s negatively impacting your life and your health or mental state
- stealing or engaging in other actions you wouldn’t ordinarily perform in order to obtain the substance
- Operating a vehicle or engaging in other hazardous tasks while under the influence of drugs
- Investing a significant amount of time obtaining the drug, taking it, or recuperating from its consequences
- Not being successful in quitting the drug
- Having withdrawal symptoms when you try to cut back on the medication